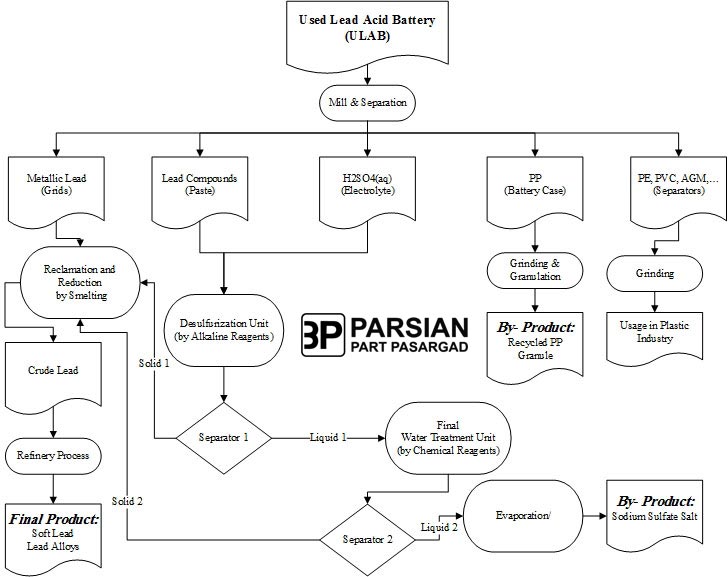
All the dumping operation of the Used Lead Acid Batteries (ULAB) will be done in the Storage Pit to avoid a dispersion of acid or lead containing material on the floor. The Storage Pit for batteries and all the floors involved in the process will be built with an underlying concrete protection layer of PE-HD to avoid the contamination of the soil with acid and lead containing material.
The batteries from Storage Pit are loaded by the Grab Bridge Crane into the Feed Conveyor and then to the primary Hammer Mill (HM1)
The materials crushed by HM1 will be fed to secondary Hammer Mill (HM2) by reducing the size of material to 30 mm. The crushed material will go through a Vibrant-Screen (VS1), and the Lead Paste and the Electrolyte screened into Thickener Tank.
The crushed fraction of plastic materials and metallic parts will be fed to a primary Hydrodynamic Separator (MS1); with the water flow utilized for the separation process, also the heavy plastics (separators, etc.) and the light plastics (Polypropylene) are discharged from the MS1 and conveyed to the primary Rotating Screen (RS1) designed for solids separation from liquid.
The plastics conveyed to the Static Separator (PLS1) by means of a screw conveyor are separated in accordance with their specific weight, made up by the floating part (Polypropylene) and by the heavy part, consisting of the other plastics (Mix Plastic).
The mixed plastic will be further separated to be sure that all the contamination of lead will be reduced at minimum by using a secondary Hydrodynamic Separator (MS2) and than dewatered through a secondary Rotary Screen (RS2).
Battery paste is de-sulphurised using sodium carbonate before being stored ready for smelting. Previously collected battery acid is also converted to sodium sulphate in the same process.
The process reaction is basically the following:
PbSO4 +Na2CO3® PbCO3 +Na2SO4
Sulphuric acid as well is part of the reaction, as follows:
Na2CO3+H2SO4® Na2SO4+H20+CO2
At the end of this process, the reactor will contain the reacted solid mass (desulphurated paste) and the liquid mass, containing the sodium sulphate solution.
Separation of the solid mass from the liquid mass is carried out by means of filter press FP1.
The solid mass (desulphurated paste) is fed to rotary furnaces and the filtered solution process will be fed in the Sodium Sulphate Crystallization unit.
The Sodium Sulphate Crystallization is based on a Forced Circulation Evaporative Crystallizer; precipitated crystals will be separated by a pusher centrifuge and dried in a vibrated fluid bed drier and then the sodium sulphate salt stored in a silo and packaging with big bag.
Two Rotary Furnaces are designed to produce crude lead from de-sulphurised paste and metallics produced by the battery breaker. These are heated by oxygen enriched, natural gas burners, designed to reduce emissions from the combustion process. A chemical flux is added to aid the conversion reaction and help remove impurities from the resultant bullion. 3P monitors the process to ensure that peak efficiency is maintained.
Lead bullion tapped from the furnace will be transferred to the Refinery Unit for next steps.
Lead bullion produced by the Foundry Unit is transferred into a processing kettle. Each kettle is capable of holding 120 tonnes of molten lead and is heated via high efficiency natural gas burners. Pyrometallurgical refining is undertaken with the lead in molten form. Refined/ Pure/ Soft Lead 99.97% is produced in accordance with the British Standard Specification EN 12588 and various Lead alloys is produced according to customer’s specification.
All the stages of the refining/ alloying process are continuously checked by an Optical Emission Spectrophotometer (OES).
The casting unit is a full automatic Casting Machine and Stacking Unit for the production of 33 Kg Ingot at continuous casting rate of 20 Tons per hour.
Polypropylene pieces separated by PLS1 in Crushing and Separation Unit is transferred to Polypropylene Recycling Unit for below processing and producing Recycled PP Granule:
1) Re- Grinding for transforming PP Pieces to PP Chips.
2) Separation other plastics and containment from PP Chips
3) Dewatering and Drying step by Centrifuge and Hot Air Fan for PP Chips
4) Storage PP Chips
6) Transforming PP Chips to PP Granule by Extruder
7) Dewatering and Drying step by Centrifuge and Hot Air Fan for PP Granule
8) Storage and Packaging PP Granule